External Otitis
External otitis or swimmer’s ear, as commonly referred to, is inflammation of the outer ear canal commonly caused by infectious agents.
What causes external otitis?
The causes are diverse as the most common infectious, but may also be due to recent contact with water, trauma, contact allergy, obstruction, hearing aids and chemical irritation. It is very important to know these causes because it helps a lot to establish the diagnosis.
What symptoms can I have if I have external otitis?
The main symptoms of external otitis are pain, itching and secretion. The pain is very characteristic of the palpation of the swallow or the mobilization of the ear. With your doctor, you can observe by otoscopy the ear canal for inflammation and redness, including pus or obstructions.
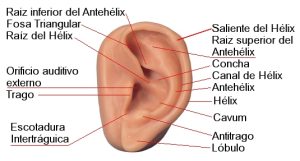
How is the diagnosis of external otitis performed?
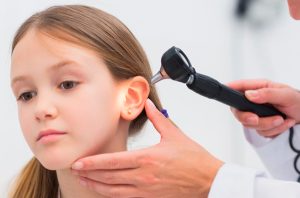
For the diagnosis are very important the antecedents (swimming in pools or ocean, use of hearing aids, trauma, etc.) and the exploration, since finding symptoms and characteristic signs do not require specialized tests to confirm the disease. Bacterial cultures can be done, but they are reserved for complicated cases.
Can external otitis have complications?
The most dangerous complication we can find is malignant external otitis (necrotizing)
What happens when the infection reaches the base of the skull (soft tissue, cartilage and temporal bone) that we remember that the separation between the base of the auditory canal and the adjacent skull is given only by a thin layer of skin.
This complication is rare and we can find it more frequently in diabetic and immunocompromised patients.
What is the treatment for external otitis?
We can find many variants of treatment, but a good guide (but not the definitive) is the following.
First clean the canal to remove any secretion or obstruction that prevents the proper administration of topical medications. In many cases only the cleaning can solve the picture.
As a second step antibiotic treatment will depend on the severity of the picture, but the standard management is done with antibiotic and steroid in drops. To help with pain and inflammation, paracetamol and naproxen can be used to reserve the use of opioid analgesics for severe cases.

How long does it take to recover?
We can find significant improvement after 36 hours of initiating treatment with a total improvement in approximately 6 days.
Remember to never self-medicate and go to the doctor in case of any symptom, but if you can not go to the physician remember that in Doctor at home PV we put a doctor to the door of your home just call us.
Source: UpToDate




