Dengue
Given the recent wave of dengue cases in Puerto Vallarta we gave the task of bringing this not so brief note so that they are informed about what it is, how it is transmitted, diagnosed, treated and prevented.
What is dengue?
It is a disease caused by a virus of RNA of the family Flaviviridae, transmitted by the mosquitoes of the species Aedes aegypti, which causes mainly fever and systemic symptoms varied being able to have severe complications even death (but only in A limited number of cases).
How is dengue transmitted?
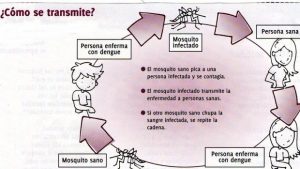
Before you understand how the disease is transmitted it is important to know the life cycle of the virus. First a healthy mosquito should be fed with the blood of an infected patient, thus the virus arrives to the intestine of the mosquito where it is replicated to infect the mosquito, now the infected mosquito when feeding on a human infects it through the saliva that it injects and thus The cycle is completed waiting for a new mosquito to do the cycle again. We can say that we must protect mosquitoes because we infect them with our blood.
Can I get dengue more than once in my life?
Yes, the reason is that there are 4 different serotypes of the dengue virus (DENV-1, 2, 3 and 4), by infecting you with some serotype, for example, in DENV-1, your immune system protects you against a new infection against that type, but there are still 3 serotypes that can infect you And then cause the disease itself or even a more serious picture.
How is dengue severity classified?
In 2009 the World Health Organization (WHO) updated the classification of dengue in 3 groups:
1-Dengue without alarm signs
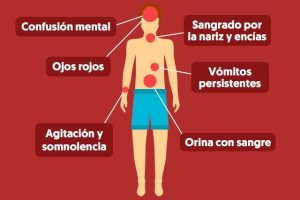
Which is defined as the presence of fever plus two of the following symptoms:
- Nausea/Vomiting
- Rash (rash or red spots on the skin)
- Headache, eye pain, muscle or joint pain
- Leukopenia (Low defense white blood cell count)
- Positive Tourniquet Test
2-Dengue with alarm signs
It is defined as a dengue without alarm signs plus any of the following symptoms:
- Abdominal Pain
- Persistent vomiting
- Clinical accumulation of fluids (in the abdomen or lungs)
- Mucosal bleeding
- Lethargy or numbness
- Hepatomegaly greater than 2 cm (liver growth)
- Increased hematocrit in biometrics hematic
3-Severe dengue
Refers to dengue virus infection plus any of the following symptoms:
- Severe plasma leakage
-Shock
-Accumulation of fluids with difficulty breathing
- Severe bleeding
- Severe organ damage
-Increase of hepatic enzymes (AST or ALT greater than 1000 u/L)
Who is at increased risk for dengue fever with signs of severe alarm and dengue?
There are several factors that can intervene in the severity of the disease and here we talk about some of the most important.
Age: It has been found that after the age of 11 years the severity of the disease is lower leaving children of this age as a vulnerable group to develop the most severe disease.

Number of infections: If you have previously had dengue a second infection with a different serotype increases the likelihood of developing severe dengue.
Diet: Studies have revealed that children who are fed breast milk are less likely to develop severe dengue compared to those who were fed formula.

Genetics: A greater number of cases have been reported, in epidemiological studies, of severe dengue in white people.
How is dengue diagnosed?
The diagnosis is suspected before a patient who has a fever adding the aforementioned symptoms that accompany the dengue and the antecedent of having traveled to areas where the disease resides, or in the case of finding ourselves in an area like Puerto Vallarta, at Presenting a patient with symptomatology the probability is high to suffer from the disease.
Currently, diagnosis is carried out not only based on clinical suspicion, with various diagnostic tools to detect the disease. The most used are the detection of viral antigen in blood or the detection of antibodies against the disease (IgM and IgG) being the detection of the antigen one of the most reliable and accessible.
How do you prevent it?
There are two ways to prevent dengue
1-Preventing the mosquito transmitter from reproducing or eliminating
With programs like “Patio Limpio” or “We are all brigades” it is sought that the mosquitoes do not find accumulations of water where to reproduce and thus reduce the population of mosquitoes. In addition, the Health Secretary Fumigates areas where infections are reported or where there is a higher population density of mosquitoes.

2-preventing mosquitoes from biting the human
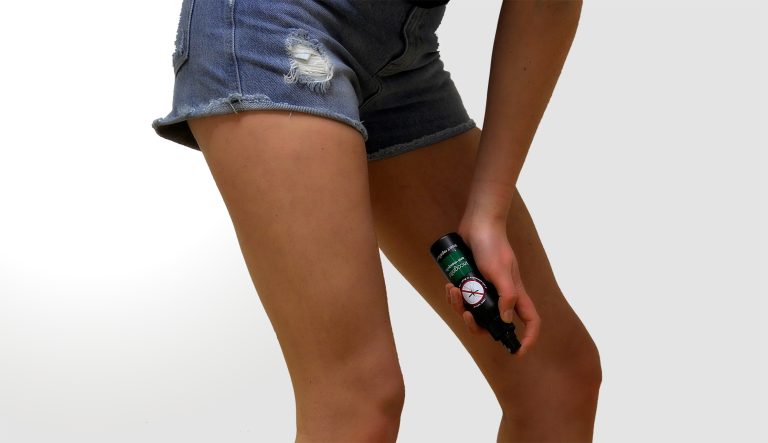
Avoiding the pickets with the use of long clothes, repellents and protective nets in the beds we avoid that the patients sick spread the infection and the healthy ones avoid to be infected.
Speaking of repellents should be looked for those containing as active ingredient N, N-diethyl-Meta-Toluamide (DEET) has demonstrated an excellent and lasting efficacy in addition to being safe to use in children and pregnant, it should be mentioned that if used in conjunction with Solar blockers can decrease the sunscreen’s protective effect. Extracts of citronella or botanical oils should be avoided since they have not been shown to be effective in scientific studies.

How is dengue treated?
Given the informative nature of this article we will limit to mention the treatment of fever and general malaise for which paracetamol is used avoiding the use of aspirin or NSAIDs (diclofenac, naproxen, metamizol, ibuprofen, etc.) since these can Increase the risk of bleeding.
Well here our brief review of what is dengue, it is important to know this information and living in Puerto Vallarta This disease is very present in the population and therefore we should be informed, always remember to call Doctor at Home PV If you suspect you may have dengue, we have what you need.
Click on this link to learn about other common diseases in Puerto Vallarta